236. Lowest Common Ancestor of a Binary Tree
Link:
Description
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to thedefinition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes v and w as the lowest node in T that has both v and w as descendants (where we allowa node to be a descendant of itself).”
_______3______ / \ ___5__ ___1__ / \ / \ 6 _2 0 8 / \ 7 4For example, the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of nodes
5and1is3. Another example is LCA of nodes5and4is5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Solution 1
子问题拆解
Bottom Up Divide and Conquer:
思考3个问题,分别在什么情况重新apply原function(这里是针对左右子树分别寻找LCA),base case是什么,要返回什么
- 针对左子树和右子树分别寻找LCA,得到left,right两个结果,可能的情况
- pq都在左边,这时右子树不包含pq,right结果应为null, left结果应该是pq在左子树的LCA,返回值为left
- pq都在右边,同i, 返回值位right
- 左子树只有p/q, 右子树只有q/p,root位LCA,返回值root,但是这时left,right的值分别为什么需要考虑,如何设计?
- 左右都不包含pq,left = right = null, 返回null
- 考虑base case:
输入root是leaf node时
- 如果root不为pq,root左右子树都为null, left = right = null, 这时根据1.iv,应该返回null
- 但是root = p/q时,left=right=null, 返回值为null就有问题了,尝试返回p/q,那么到上一层调用里如何处理?
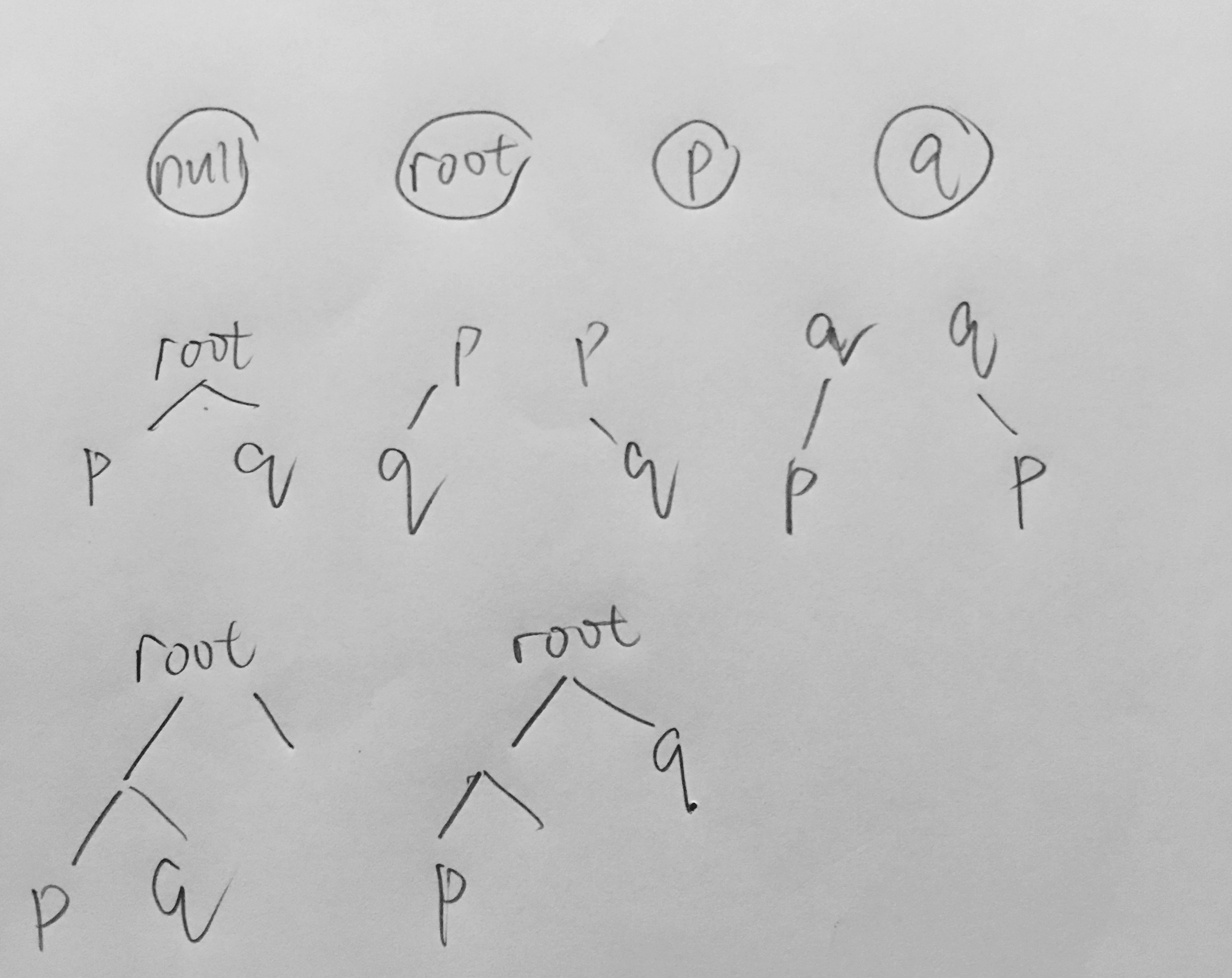
- 1.iii 和 2.ii 综合考虑,得到思路,见图1,当只能找到p/q的时候,把p/q往上返回,直到某一层,p/q分别在left/right里面,返回root,或者root位p/q, left和right一个为null另一个为q/p, 还是返回root满足1.iii和2.ii的要求
- root = null/p/q是返回root, left,right都不为null时返回root, 都为null返回null,只有一边为null返回另一边(LCA)
过程可视化

打破假设
类比
Code
//Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root == null || root == p || root == q)
return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if(left != null & right != null)
return root;
if(right != null)
return right;
if(left != null)
return left;
return null;
}
}
Analysis
Reference
Solution2
子问题拆解
- 暴力直觉:找到root到p和q的路径,然后从路径中找LCA
- 考虑用map记录每个node的parent
- 从p开始,顺着parent走到root,并记录路径
- 从q考试顺着parent往上走,看哪个parent在3的路径里,走到root就返回root
- 完成,优化第三部可以用set, 优化2可以traverse到pq都找到就停止
过程可视化
打破假设
类比
Code
//Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
HashMap<TreeNode, TreeNode> parent = new HashMap<>();
stack.push(root);
parent.put(root, null);
while(!stack.empty() || !parent.containsKey(p) || !parent.containsKey(q)){
TreeNode node = stack.pop();
if(node.left != null){
stack.push(node.left);
parent.put(node.left, node);
}
if(node.right != null){
stack.push(node.right);
parent.put(node.right, node);
}
}
HashSet<TreeNode> path = new HashSet<>();
while(p != null){
path.add(p);
p = parent.get(p);
}
while(q != null){
if(path.contains(q))
return q;
else
q = parent.get(q);
}
return null;
}
}